Top 10 Industrial Steel Applications Transforming Modern Industries?
Industrial steel has become a cornerstone in modern industries, driving innovation and efficiency. According to a report by the World Steel Association, global steel production reached over 1.8 billion tonnes in 2021. This figure illustrates the growing demand for industrial steel across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Expert Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned industrial steel analyst, stated, "Industrial steel is not just a material; it's a foundation for progress." This paradigm shift is evident in how industries leverage advanced steel applications for sustainability and performance. The automotive sector, for instance, has increasingly adopted high-strength steel to enhance vehicle safety while reducing weight.
However, challenges remain. Many companies struggle to integrate innovative steel solutions into their practices. The gap between potential and application needs careful consideration. Some industries still rely on outdated processes, hindering growth. As the industrial steel landscape evolves, businesses must adapt to harness its full potential. The future of industries heavily depends on the strategic implementation of industrial steel technologies.

Top 10 Industrial Steel Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
Steel plays a vital role in automotive manufacturing. Its strength and durability make it ideal for various vehicle components. For instance, the chassis and frames rely heavily on steel for support and safety. This material can withstand significant stress, ensuring that vehicles remain intact during accidents. However, the use of steel isn't without challenges. It can be heavy, which impacts fuel efficiency.
In recent years, manufacturers have explored alternatives. Lighter materials like aluminum or composites are gaining traction. Yet, they may not offer the same strength as steel. Steel's recyclability is another key aspect. Most steel in cars can be reclaimed, reducing waste. Still, the recycling process can be energy-intensive and requires careful management.
Another area for improvement is the production process itself. Innovations in steel production aim to reduce carbon emissions. These changes may make steel a more sustainable choice in the long run. Nevertheless, the industry must address its legacy of high emissions. Balancing performance, sustainability, and cost is an ongoing conversation in automotive steel applications. The pursuit of perfect materials remains elusive.
Top 10 Industrial Steel Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
| Application | Description | Material Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chassis Components | Structural framework providing support and stability. | High-Strength Steel | Enhanced durability and reduced weight. |
| Body Panels | Outer skin that affects aesthetics and aerodynamics. | Mild Steel | Cost-effective and good formability. |
| Suspension Systems | Components that absorb shocks and improve handling. | Spring Steel | High elasticity and strength under load. |
| Powertrain Systems | Includes drivetrain components and support structures. | Alloy Steel | Improved performance and durability under stress. |
| Safety Features | Includes crumple zones and reinforcements. | Dual-Phase Steel | High energy absorption during crashes. |
| Exhaust Systems | Includes pipes and mufflers for emission control. | Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance and durability. |
| Braking Systems | Components vital for vehicle deceleration. | Martensitic Steel | High strength and wear resistance. |
| Fuel Tanks | Storage for automotive fuel. | Coated Steel | Prevention of corrosion and leakage. |
| Wheels | Critical component for vehicle mobility. | Forged Steel | High strength and lightweight construction. |
Innovations in Construction: Steel's Role in Sustainable Building Practices

The construction industry is undergoing significant changes with steel at the forefront. Steel's strength and durability make it an ideal choice for modern buildings. Innovative designs now incorporate steel elements that reduce the carbon footprint. Buildings made from steel can be lighter yet stronger, providing more usable space. This efficiency is critical as cities grow denser.
Sustainable practices are evolving. Recycled steel is increasingly popular in new constructions. It reduces waste and utilizes existing materials. However, reliance on steel must be balanced. Its production is energy-intensive and can release high emissions. Finding greener methods for steel manufacturing is essential. This requires collaboration and innovation within the industry.
The role of steel touches every aspect of construction. From framing to finishes, it offers versatility. But challenges persist. Over-reliance on steel may lead to structural weaknesses if not monitored. Regular assessments are needed to maintain safety and sustainability. Engaging stakeholders to rethink steel’s role in construction can pave the way for better practices.
Steel in Energy: Transforming Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Steel plays a pivotal role in the evolution of renewable energy infrastructure. With global renewable energy production expected to increase by 50% by 2030, steel's importance cannot be overstated. It is used extensively in wind turbines and solar panel frameworks. In fact, a single onshore wind turbine can require around 200 tons of steel, showcasing its significant role in construction.
The demand for robust, durable materials is rising. Industry reports indicate that the steel market for energy applications will surpass $200 billion by 2025. However, challenges remain in sourcing sustainable steel. Many manufacturers still rely on traditional methods, which contribute to carbon emissions. The industry must pivot towards greener methods, like electric arc furnaces, which could reduce emissions by up to 75% compared to conventional processes.
Innovation is also critical. Advanced steel alloys are being developed to withstand higher temperatures and pressures, enhancing efficiency in renewable applications. Nevertheless, the transition is slow. Quality control and supply chain sustainability pose ongoing challenges. The journey towards a greener energy future depends significantly on addressing these issues while leveraging the advantages that steel offers.
Top 10 Industrial Steel Applications Transforming Modern Industries
Steel in Energy: Transforming Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Advanced Steel Alloys in Aerospace Engineering Applications
In aerospace engineering, advanced steel alloys play a critical role. These materials bring strength and lightweight properties. They enable aircraft to withstand harsh conditions while improving fuel efficiency. High-strength steel is often combined with other elements. This creates alloys that resist fatigue and corrosion.
The applications are vast. Components like landing gear and engine mounts require robust materials. The design process is complex. Engineers must balance weight with strength. Even minor mistakes can lead to significant issues. Testing and refinement become crucial in this industry. Each alloy must be thoroughly assessed before use.
Innovation often brings challenges. New steel formulations can behave unpredictably under stress. Research is ongoing to improve performance and durability. There’s always room for improvement. The quest for lighter, stronger materials continues to reshape aerospace engineering. As technology advances, these alloys will drive the next generation of aircraft design.
The Impact of Steel on Manufacturing Efficiency and Productivity Trends
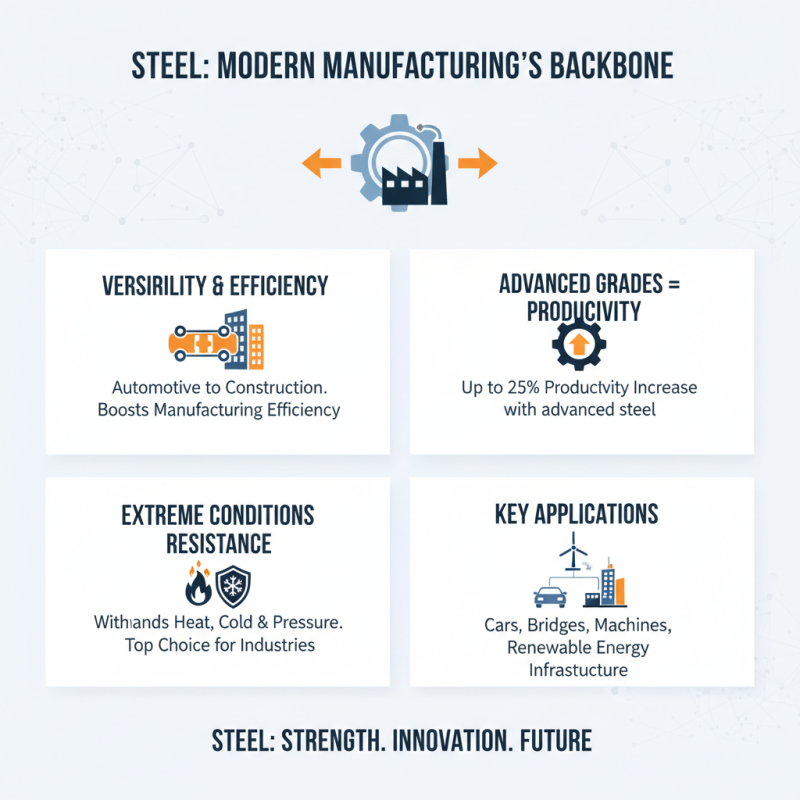
Steel plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing. Its applications range from automotive to construction. The versatility of steel enhances manufacturing efficiency. Recent studies show that using advanced steel grades can improve productivity by up to 25%. The ability to withstand extreme conditions makes steel a top choice for industries.
Manufacturers face challenges when integrating new steel technologies. Not all facilities can adapt quickly to these innovations. Furthermore, the initial costs for advanced steel solutions can be high. A report from Industry Week highlights that 30% of manufacturers struggle with supply chain issues, which can delay steel production. This disrupts efficiency and impacts overall productivity.
Moreover, sustainability is a growing concern. Steel production is energy-intensive. The carbon footprint of steel manufacturing is significant. Analysts emphasize that improving energy efficiency in steel production could reduce emissions by 20%. However, many companies are still hesitant to invest in these improvements. Balancing cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility remains a significant challenge.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Growth of Industrial Steel Demand at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

2025 Top 5 Wire Steel Innovations Transforming the Industry
-

Understanding the Benefits of Using Cold Drawn Steel Bars in Modern Construction
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Wire Rod
-
Top 10 Steel Rod Specifications You Need to Know for Your Projects
-

The Versatile Applications of Stainless Steel Wire Rod in Modern Industries
