How to Choose the Right Steel Grades for Your Project?
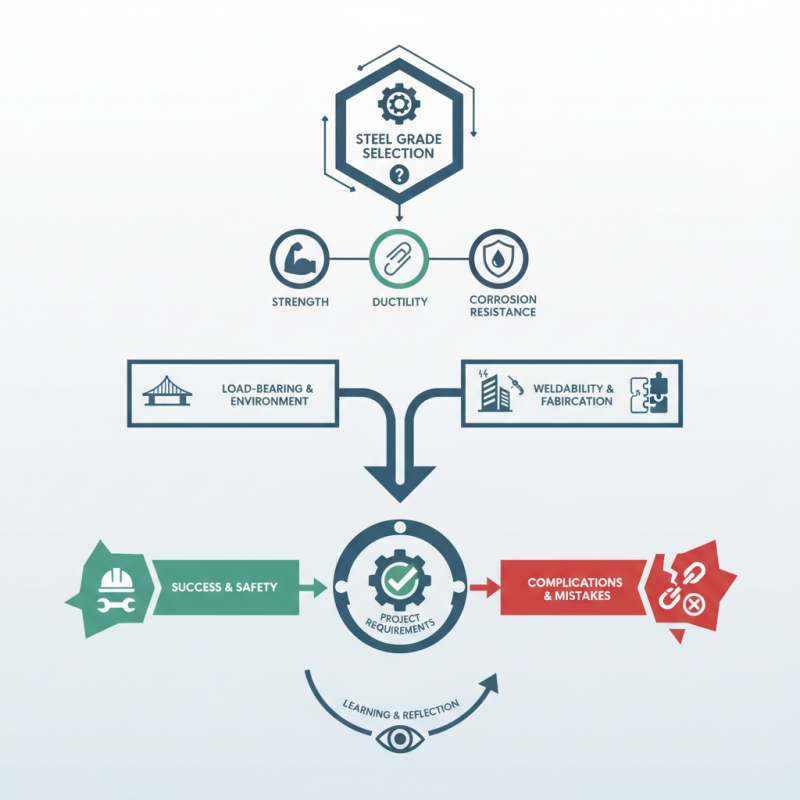
Choosing the right steel grades for a project can be daunting. Steel is a versatile material, but not all grades suit every application. Each grade possesses unique properties, like strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. These factors influence the finished product's performance and longevity.
When selecting a steel grade, consider the specific requirements of your project. Think about load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions. Some projects may require high tensile strength, while others might prioritize weldability or fabrication ease. The right choice ultimately affects safety and functionality.
Keep in mind that mistakes can happen. Misjudging a project's needs or overlooking a critical steel grade can lead to complications. Reflecting on past experiences can inform your decision-making process. Understanding and selecting steel grades is essential for successful project outcomes.
Understanding Steel Grades: An Overview of Common Classifications
Steel is essential in various industries, but its quality varies significantly. Understanding steel grades helps in selecting the right material for your project. Steel grades are categorized mainly into carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and tool steel, each serving specific purposes.
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides standard classifications. For example, ASTM A36 is common for structural applications, while ASTM A992 is preferred for high-rise buildings due to its high yield strength. Alloy steels offer enhanced properties, like improved toughness or resistance to wear. Stainless steels, like 304, are great for corrosive environments.
Here are some tips. Check the mechanical properties. Look for yield strength and tensile strength data. High tensile strength is crucial for load-bearing structures. Also, consult relevant codes and standards. They provide valuable insights into material requirements.
Another reflection point is cost versus performance. Higher grades may cost more but offer longevity. A cheaper alternative might lead to frequent replacements. Assess the long-term impact. Well-informed choices save money and time in the long run.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Steel Grades for Your Project

Selecting the right steel grades is crucial for project success. Various factors come into play when making this decision. The type of construction, the environment, and the load-bearing requirements all matter. According to a report by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), specific grades provide distinct mechanical properties. For instance, while ASTM A36 might be fine for general construction, it falls short for high-stress applications.
Another key factor is corrosion resistance. Projects near coastal regions demand higher-grade steel, such as ASTM A992. It offers enhanced durability against salt and moisture. The cost is a significant consideration too. Higher grades usually come with a premium price tag. It’s essential to balance quality and budget. A study from the Steel Construction Institute indicates that 30-40% of project costs often stem from material choices.
It’s also critical to think about availability. Certain grades might have longer lead times, complicating project timelines. Not considering this might lead to delays. Sometimes, engineers overlook grade selection entirely, which can lead to structural failures. In one case, the selection of an inappropriate grade led to costly repairs. Learning from such oversights is vital for future projects. Evaluating all these factors will steer you toward a more informed decision.
The Importance of Mechanical Properties in Steel Grade Selection

When selecting steel grades for a project, understanding mechanical properties is crucial. These properties determine how the steel will behave under stress, heat, or various environmental conditions. Tensile strength, for instance, measures how much load the steel can handle without breaking. Including this is vital when designing structures that must withstand heavy loads.
Another important property is ductility. It indicates how much a material can stretch before it fails. In construction, ductile steel can absorb energy and deform rather than fracture suddenly. This can be a lifesaver in seismic zones. However, it’s easy to overlook such details during the selection process. Many assume all steel is similar.
Not all grades suit every purpose. High carbon steel is strong but can be brittle, making it unsuitable for certain applications. On the other hand, low-carbon steel is more malleable but lacks strength. Balancing these properties requires careful thought and sometimes compromise. Testing different grades in real conditions can often reveal surprises. It is a mix of study and trial, leading to better choices in the long run.
Applications of Various Steel Grades Across Different Industries
Choosing the right steel grade is crucial for various industries. For construction, structural steel grades like S235 and S355 are commonly used. They provide high strength and durability. According to the World Steel Association, these grades account for over 80% of steel used in construction projects.
In manufacturing, stainless steel grades such as AISI 304 and 316 are popular. These grades resist corrosion and high temperatures. The global demand for stainless steel has increased by 8% annually due to its applications in kitchenware and medical equipment. However, some projects require careful consideration of cost versus performance.
In the automotive industry, high-strength low-alloy steels are key. They offer weight reduction without sacrificing safety. Automotive applications use approximately 60% of the world's steel. This reliance can lead to supply chain challenges, affecting project timelines. Understanding the specific requirements and limitations of each steel grade can be a complex task that requires ongoing research and reflection in project planning.
How to Choose the Right Steel Grades for Your Project?
This chart illustrates the applications of various steel grades across different industries. Understanding these applications can help in selecting the right steel grade for your specific project needs.
Testing and Certification: Ensuring Quality in Steel Grade Verification
Selecting the right steel grade is critical for any project. However, quality assurance is equally important. Testing and certification ensure that the steel meets necessary standards. Without verification, even high-grade steel can fail.
Various testing methods exist. Tensile strength tests measure how much force the steel can withstand without breaking. Impact tests check resilience against sudden forces. Both are vital for ensuring safety in structural applications. But these tests are only as good as their execution. Inadequate procedures can lead to inaccurate results.
Certification bodies assess steel products against industry standards. They provide a stamp of approval that indicates compliance. However, not all certifications are created equal. Some may lack rigorous testing. It's crucial to research the certifying entity. Ensuring transparency in the certification process can prevent future headaches. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that the chosen steel will perform as expected.
Related Posts
-

Steel Grades Innovations Showcased at 2025 China 138th Import and Export Fair with Industry Data Insights
-

Exploring the Future of Carbon Steel: Insights from the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

What is Carbon Steel and How is it Different from Other Steels
-

2025 Top 5 Wire Steel Innovations Transforming the Industry
-

Top 10 Industrial Steel Applications Transforming Modern Industries?
-

Top 5 Reasons Why Wire Steel is Essential in Construction and Manufacturing
